Explore the Power of the Aeroponic System
Contents
- 1 Explore the Power of the Aeroponic System
- 1.1 Aeroponic System: The Future of Sustainable Farming
- 1.2 Benefits of Aeroponic Systems in Sustainable Farming
- 1.3 Comparison of Aeroponics with Traditional Farming Methods
- 1.4 How Aeroponic Systems Work
- 1.5 Challenges and Limitations of Aeroponic Systems
- 1.6 The Future of Sustainable Farming with Aeroponics
- 1.7 Implementing Aeroponic Systems on Your Farm
- 1.8 Resources and Tools for Aeroponic Farming
- 1.9 Conclusion to Aeroponic System
- 1.10 Aeroponic vs Hydroponic Systems: A Comparative Guide
Aeroponic System: The Future of Sustainable Farming
 Welcome to the future of sustainable farming! In this article, we will explore the power of aeroponic systems and how they shape how we grow our food. With a maximum word limit, let’s dive right in. Imagine a farming method that requires less water, eliminates the need for soil, and maximises crop yields. That’s exactly what aeroponic systems offer. By misting plant roots with a nutrient-rich solution, plants receive optimal nutrition while using significantly less water than traditional farming methods.
Welcome to the future of sustainable farming! In this article, we will explore the power of aeroponic systems and how they shape how we grow our food. With a maximum word limit, let’s dive right in. Imagine a farming method that requires less water, eliminates the need for soil, and maximises crop yields. That’s exactly what aeroponic systems offer. By misting plant roots with a nutrient-rich solution, plants receive optimal nutrition while using significantly less water than traditional farming methods.
This innovative technology conserves resources and ensures consistent and healthy plant growth. Aeroponic systems are revolutionising the way we approach agriculture, making it possible to grow fresh produce in urban environments, deserts, and even space.
From leafy greens to flavourful herbs, aeroponics allows farmers to cultivate a wide range of crops with minimal environmental impact. And the best part? These systems can be tailored to fit any scale – from small urban gardens to large commercial operations.
Join us as we explore the exciting potential of aeroponic systems and the ways they are paving the path for a sustainable and efficient future of farming.
Benefits of Aeroponic Systems in Sustainable Farming
Aeroponic systems are a type of soilless cultivation that uses mist or fog to deliver nutrients and water to the roots of plants. Aeroponic systems have many benefits for sustainable farming, such as:
-
-
- Saving water and fertiliser: Aeroponic systems use up to 95% less water and 60% less fertiliser than conventional soil-based farming, as the mist or fog can be recycled and reused, and the nutrient solution can be precisely controlled and adjusted.
- Reducing pests and diseases: Aeroponic systems eliminate the need for soil, which can harbour pathogens, weeds, and pests that can harm plants. This reduces the use of pesticides and herbicides, which can have negative impacts on the environment and human health.
- Increasing yield and quality: Aeroponic systems allow for optimal aeration and oxygenation of the roots, which can enhance the growth and development of the plants. Aeroponic systems can also produce higher-quality crops, as they are less prone to stress, damage, or contamination from soil or water.
- Saving space and energy: Aeroponic systems can be designed to fit in small or vertical spaces, which can increase land use efficiency and reduce transportation costs and emissions. Aeroponic systems can also use renewable energy sources, such as solar or wind power, to operate the pumps and fans that create the mist or fog.
-
Comparison of Aeroponics with Traditional Farming Methods
Aeroponics is a method of growing plants without soil, using a mist of nutrient solution to deliver water and minerals to the roots. Traditional farming methods, on the other hand, rely on soil as the main medium for plant growth and nutrient uptake. In this paragraph, we will compare the advantages and disadvantages of aeroponics with traditional farming methods.
One of the main advantages of aeroponics is that it uses less water and space than traditional farming methods. Aeroponics can save up to 95% of water compared to soil-based agriculture, as the mist is recycled and reused in a closed-loop system. Aeroponics also allows for higher plant density and vertical stacking, which can increase the yield per unit area. Furthermore, aeroponics eliminates the need for pesticides and herbicides, as the plants are not exposed to soil-borne diseases or weeds.
However, aeroponics also has some disadvantages that limit its widespread adoption. Aeroponics requires more energy and technical expertise than traditional farming methods, as it depends on pumps, nozzles, sensors, and timers to maintain optimal conditions for plant growth. Aeroponics also poses a higher risk of crop failure, as any malfunction or power outage can result in rapid dehydration and death of the plants. Additionally, aeroponics may not be suitable for all types of crops, especially those that require pollination or have deep roots.
How Aeroponic Systems Work
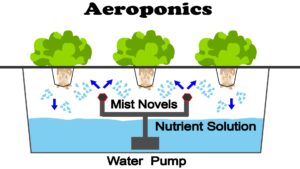
Aeroponic systems are a type of hydroponic system that uses mist or fog to deliver water and nutrients to the roots of plants. Unlike traditional hydroponics, aeroponics does not require any growing medium, such as soil, rockwool, or perlite. Instead, the plants are suspended in the air, with their roots exposed to the mist. This allows for greater oxygenation of the roots, which can enhance plant growth and health.
Aeroponic systems consist of a reservoir, a pump, a misting device, and a chamber or enclosure. The reservoir holds the nutrient solution, which is pumped into the misting device. The misting device can be a nozzle, a sprinkler, or an ultrasonic fogger, depending on the size and type of the system. The misting device sprays the nutrient solution as fine droplets into the chamber or enclosure, where the plants are located. The chamber or enclosure can be a box, a tube, a tower, or any other structure that can hold the plants and prevent light from reaching the roots.
The benefits of aeroponic systems include:
-
-
- Reduced water and nutrient consumption, as the mist is recycled and reused in the system.
- Reduced risk of pests and diseases, as there is no soil or growing medium to harbour pathogens or insects.
- Increased plant growth and yield, as the roots have access to more oxygen and nutrients.
- Increased flexibility and versatility, as the system can be adapted to different plants and environments.
-
The challenges of aeroponic systems include:
-
-
- Higher initial cost and maintenance, as the system requires more equipment and components than other hydroponic systems.
- Higher risk of failure, as the system depends on electricity and pumps to function. If the power goes out or the pump breaks down, the plants can quickly dry out and die.
- Higher technical skill and knowledge are required, as the system requires precise control and monitoring of the nutrient solution, pH, temperature, humidity, and mist frequency.
-
Challenges and Limitations of Aeroponic Systems
Aeroponic systems are a form of soilless cultivation that uses pressurised mist to deliver nutrients and water to plant roots suspended in the air. Aeroponic systems offer several advantages over conventional methods, such as higher yields, lower water consumption, reduced pest and disease risks, and greater control over environmental factors. However, aeroponic systems also face some challenges and limitations that need to be addressed for their successful implementation. Some of these challenges include:
-
-
- High initial costs of setting up the system, including the purchase of pumps, nozzles, sensors, and other components.
- High maintenance requirements and constant monitoring of the system parameters, such as nutrient solution concentration, pH, temperature, humidity, and mist frequency.
- High dependency on electricity and risk of system failure due to power outages or technical malfunctions.
- The high complexity of the system design and operation requires skilled personnel and adequate training.
- Potential environmental impacts of nutrient runoff, noise pollution, and greenhouse gas emissions.
-
Therefore, aeroponic systems require careful planning, optimisation, and innovation to overcome these challenges and limitations and achieve their full potential in sustainable agriculture.
The Future of Sustainable Farming with Aeroponics
Aeroponics is a method of growing plants without soil, using a mist of water and nutrients to deliver them to the roots. This technique has many advantages over traditional farming, such as saving water, reducing land use, preventing soil erosion, and increasing crop yields. Aeroponics also allows for more control over the growing environment, such as temperature, humidity, and light, which can improve the quality and health of the plants.
The future of sustainable farming with aeroponics is promising, as it can address some of the major challenges facing agriculture today, such as climate change, food security, and urbanisation. Aeroponics can be adapted to different climates and locations, such as rooftops, greenhouses, or vertical farms. It can also produce fresh and local food all year round, reducing the need for transportation and storage. Aeroponics can also contribute to biodiversity conservation, as it does not require pesticides or herbicides that can harm the ecosystem.
Aeroponics is not only a sustainable way of farming, but also a profitable one. According to a report by Grand View Research, the global aeroponics market size was valued at USD 578.7 million in 2018 and is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 25.6% from 2019 to 2025. The demand for aeroponics is driven by factors such as rising population, urbanisation, and consumer awareness of the benefits of organic food. Aeroponics also offers lower operational costs and higher returns on investment than conventional farming methods.
Aeroponics is a revolutionary technology that can transform the future of sustainable farming. By using aeroponics, farmers can produce more food with fewer resources, while protecting the environment and enhancing human health. Aeroponics is not only a viable solution for the present, but also a vision for the future.
Implementing Aeroponic Systems on Your Farm
Aeroponic systems are a type of hydroponic system that uses mist or fog to deliver water and nutrients to the roots of plants. Aeroponic systems have many advantages over traditional soil-based farming, such as higher yields, lower water consumption, less space requirement, and reduced risk of pests and diseases. In this article, we will explain how to implement aeroponic systems in your farm, and what the main challenges and benefits of doing so.
-
-
- The first step to implementing aeroponic systems in your farm is to design the layout and structure of the system. You will need to consider factors such as the size and shape of your growing area, the number and type of plants you want to grow, the climate and weather conditions, the power source and availability, and the budget and maintenance costs. You will also need to choose the appropriate components for your system, such as the reservoir, pump, timer, misters, nozzles, pipes, fittings, sensors, controllers, and growing media.
- The second step is to assemble and install the system according to your design. You will need to follow the instructions and safety precautions provided by the manufacturer or supplier of your components. You will also need to test the system for leaks, pressure, flow rate, and spray pattern before planting your crops. You will need to adjust the settings and parameters of your system according to the specific needs of your plants, such as the pH level, electrical conductivity, nutrient concentration, mist frequency and duration, temperature, humidity, and light.
- The third step is to monitor and maintain your system regularly. You will need to check the water level and quality in your reservoir and replenish or replace it as needed. You will also need to clean and sanitise your system periodically to prevent clogging, algae growth, bacterial contamination, and fungal infection. You will need to prune and harvest your crops according to their growth cycle and maturity. You will also need to troubleshoot any problems or issues that may arise with your system or plants.
-
Implementing aeroponic systems in your farm can be a rewarding and profitable venture if done correctly. Aeroponic systems can produce high-quality crops with fewer resources and environmental impact than conventional farming methods. However, aeroponic systems also require careful planning, installation, operation, and maintenance to ensure optimal performance and results. By following these steps, you can successfully implement aeroponic systems on your farm.
Resources and Tools for Aeroponic Farming
Aeroponic farming is a method of growing plants without soil, using a mist of water and nutrients to deliver oxygen and minerals to the roots. Aeroponic farming has many advantages over traditional soil-based agriculture, such as higher yields, lower water consumption, reduced pest and disease problems, and more efficient use of space. However, aeroponic farming also requires specialised resources and tools to ensure optimal plant growth and health. Some of the essential resources and tools for aeroponic farming are:
-
-
- A suitable growing chamber or tower that can support the plants and provide adequate air circulation and light exposure.
- A high-pressure pump and nozzle system can create a fine mist of water and nutrients for the roots.
- A reservoir or tank that can store the nutrient solution and regulate its pH, temperature, and electrical conductivity.
- A timer or controller that can automate the misting cycle and adjust it according to the plant’s needs.
- A monitoring device or sensor that can measure the environmental conditions and the nutrient solution parameters.
- A backup power source or generator that can prevent interruptions in the misting cycle due to power outages.
- A ventilation system or fan that can prevent overheating and humidity build-up in the growing chamber or tower.
- A harvesting tool or scissors that can cut the plants without damaging the roots.
-
These are some of the basic resources and tools for aeroponic farming, but there may be other specific requirements depending on the type of plants, the scale of production, and the desired quality of the harvest. Aeroponic farming is a promising technology that can offer many benefits for food security, sustainability, and innovation, but it also requires careful planning, management, and maintenance to ensure its success.
Conclusion to Aeroponic System
Aeroponic systems are a promising technology for sustainable and efficient food production. Aeroponic systems use mist or fog to deliver nutrients and water to the roots of plants, reducing water consumption, soil erosion, and pest infestation. Aeroponic systems also allow for greater control over environmental conditions, such as temperature, humidity, and light, enhancing the quality and yield of the crops. Aeroponic systems are suitable for urban and vertical farming, as they require less space and energy than conventional methods. Aeroponic systems have the potential to address the challenges of food security, climate change, and resource depletion in the future.

Pingback: Aeroponic vs Hydroponic Systems: A Comparative Guide
Pingback: The Ultimate Guide to Hydroponic Lighting Systems